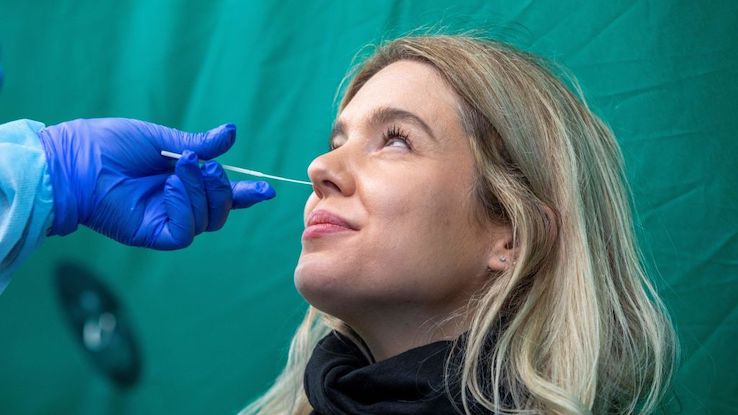
COVID-19 testing has become part of the new normal. Maybe you have symptoms and want to know if it’s COVID-19. Or you’re planning on traveling and need to show negative test results. Whatever your reason for testing, you may be wondering about a PCR vs. antigen test and which type is right for you.
Molecular tests, including polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests, are more accurate. But they usually go through a laboratory, so it takes longer to get your results. Antigen tests (also called rapid tests) are less accurate, but you can do them at home and get results in about 15 minutes. Read more to decide which type is right for you.
How Do PCR and Other Molecular Tests Work?
Molecular tests use a laboratory process to look for the genetic material of the virus that causes COVID-19. PCR and other molecular tests can find even small amounts of the virus, so they have very few false negative results.
You can get PCR tests at health clinics, pharmacies, and other designated testing locations. They usually involve a nasal swab, but can also use a throat swab or saliva sample. After your sample is collected, it’s sent to a laboratory for processing. It usually takes between one and seven days to get PCR test results. There are also home collection PCR kits you can use to send a sample via mail to a laboratory.
Can You Get a Same-Day PCR Test?
If you want a PCR test but need your results right away, there are same-day PCR test locations that can provide results within a few hours. Same-day PCR testing may be offered by small diagnostic or urgent care clinics. You can search online for same-day PCR testing near you.
Another option is a rapid molecular test called ID NOW. This test is not as sensitive as a laboratory PCR test, but it’s more sensitive than an antigen test. Certain pharmacies offer this test, and you can get your results on site in as little as 15 minutes.
How Do Antigen Tests Work?
Antigen tests look for viral proteins instead of the genetic material of the virus. They can’t detect very small amounts of virus, so you need a higher amount of the virus in the sample to get a positive result. That means you’re most likely to get an accurate result when you have the most virus in your system (typically about a week after symptoms appear).
This also means that false negative results are more common with antigen tests, especially if you’re asymptomatic (meaning you’re infected but don’t have any symptoms) or if you take the test when you were recently infected.
Unlike PCR tests, you can do the entire antigen test process by yourself at home. You simply take a nose or throat swab and apply the swab to a cartridge or test strip, similar to a pregnancy test. Results are usually ready in about 15 minutes. That’s why these are often called “rapid” tests. You can also get rapid antigen tests at doctors’ offices and pharmacies.
PCR vs. Antigen Test: Which Should I Choose?
The type of test you need depends on the reason you’re taking it. For example, doctors usually use PCR tests to confirm a COVID-19 diagnosis because they’re more accurate. But if you’re doing routine testing through your school or workplace, antigen tests are probably more convenient and effective for quick, regular tests.
If you’re planning on traveling, you may be required to show a negative COVID-19 test. Depending on where you’re going, there may be requirements for the type of test as well as when and where you get it. So make sure you know the rules for the area you’re visiting to avoid any delay in your plans.
If you’re sick and have symptoms of COVID-19, a drive-thru PCR test or home antigen test may be a good choice so that you avoid the risk of exposure to others. Many people also take COVID-19 tests for peace of mind. Whatever your reason, it’s important to consider the timing. Experts recommend that you wait three to five days after a potential exposure to avoid a false negative result.
Where Can I Get Tested Near Me? And What About Cost?
Health centers and pharmacy chains like CVS and Walgreens provide COVID-19 tests for little or no cost. Testing may also be covered by your insurance at approved locations like hospitals or doctors’ offices. But at-home rapid antigen tests may not be covered. So if cost is a concern, do your research and check with your insurance company before choosing a test type and location — or find a free community testing location near you.
And if you have symptoms of COVID-19, talk with your doctor and follow their recommendations for testing and managing your symptoms.
And remember, the best way to protect yourself and others from COVID-19 is to get vaccinated. Learn more about COVID-19 vaccines and how to get them.
Resource Links
- “COVID-19 Diagnostic Testing” via Mayo Clinic
- “Which COVID-19 Test Should You Use?” via Yale Medicine
- “Coronavirus Disease 2019 Testing Basics” via Food and Drug Administration
- “Five Things to Know About the Cost of COVID-19 Testing and Treatment” via Kaiser Family Foundation





